Integrate Fortinet-FortiGate
This technical integration guide describes how to integrate a Fortinet-Fortigate and Identity as a Service. The aim of this integration is to provide strong, second-factor authentication for your Fortinet-Fortigate VPN solution using Identity as a Service.
Note: Some configuration steps may differ from the documentation provided or the steps in this integration guide may not be effective (due to Entrust not having tested and validated with the version you are using). For different versions, this integration guide may still offer a standard base to help fast-track SAML authentication setup for your application, but in the event there are issues, contact support@entrust.com for assistance.
The Fortinet-Fortigate software supports the Identity as a Service authentication methods and authentication protocols listed in the table below. The capabilities may depend on the Identity as a Service configuration, or the setup of other 3rd party authentication resources (Active Directory, for example).
Supported authentication methodsSupported authentication methods
Note: For Fortinet RADIUS authentications, Entrust suggests using PAP or CHAP authentication for two-step Entrust authentication and MSCHAPV1 or MSCHAPv2 for one-step Entrust token authentication. The EAP authentication protocol is not supported.
| Authentication method | Notes | Supported protocols |
|
Password |
Password authentication is first-factor authentication with Identity as a Service password feature. |
PAP, CHAP |
|
RADIUS |
RADIUS authentication is first-factor authentication with a RADIUS server. |
PAP, CHAP |
|
External |
External authentication is first-factor authentication with an LDAP-compliant directory or a Windows domain controller through Kerberos. |
PAP, CHAP |
|
Grid |
Two-step authentication only. |
PAP, CHAP |
|
Token |
Identity as a Service supports response-only tokens. One-step and Two-step authentication (including push). |
PAP, CHAP, MSCHAPv1, MSCHAPv2 |
|
Temporary Access Code |
Grid or token authentication must be configured. |
PAP, CHAP, MSCHAPv1, MSCHAPv2 |
|
One-time password |
Two-step authentication only. |
PAP, CHAP |
|
Knowledge-based questions and answers |
The RADIUS proxy only supports a single question and answer. Two-step authentication only. |
PAP, CHAP |
|
Mobile Soft Token |
Mobile Soft Token push authentication (supports response-only tokens for second-factor authentication). |
PAP, CHAP |
PrerequisitesPrerequisites
Complete the following steps before integrating your authentication system with Identity as a Service:
Install and configure your first-factor authentication resource using the documentation provided by the vendor. The first-factor authentication resource can be a RADIUS server or an external authentication resource (a Local DB, LDAP-compliant directory or Windows domain controller through Kerberos).
Install and configure the RADIUS appliance using the documentation provided by the vendor. The device must be able to route traffic before integrating with Identity as a Service.
Install and configure Identity as a Service and an Identity as a Service Gateway (containing a RADIUS proxy agent). Take note of the shared secrets, IP addresses, and ports you use. You need this information to configure the RADIUS appliance and first-factor authentication resource.
If you want to configure your RADIUS appliance and first-factor authentication resource to recognize Identity as a Service user groups, you must define the Identity as a Service user groups first.
Integrate Fortinet-FortiGate VPN
Complete the following steps to integrate FortiNet-FortiGate VPN with IDaaS:
Step 1: Start the Fortinet-FortiGate configuration utility
Before you configure Fortinet-FortiGate and manage the system, you need to connect the unit to a management workstation or network.
Start the Fortinet-FortiGate configuration utilityStart the Fortinet-FortiGate configuration utility
Start the Configuration utility in a web browser
After you connect the management workstation to the FortiGate management interface, in a Web browser, open the Configuration utility and launch the configuration system by typing the following URL syntax where <https://management_IP_address> is the IP address you configured for FortiGate device management.
At the login prompt, enter the default user name admin, and password.
The Fortinet FortiGate Web GUI opens, which allows you to configure the unit.
Step 2: Configure the FortiGate unit to use IDaaS
There are three steps to integrate the Fortinet-FortiGate with Entrust Identity as a Service and setup the SSL/IPSec Remote Access VPN. Complete all the steps.
Step 2a: Create a new RADIUS serverStep 2a: Create a new RADIUS server
To use IDaaS authentication with a FortiGate unit, configure one or more RADIUS servers on the FortiGate unit and assign users to a RADIUS server. When a configured user attempts to access the network, the FortiGate unit forwards the authentication request to IDaaS, which matches the username and password remotely. Once authenticated, IDaaS passes the authentication to the FortiGate unit, which then grants the user permission to access the network.
In the FortiGate Web console, navigate to User & Device > RADIUS Servers and click Create New. The Create RADIUS Server page appears.
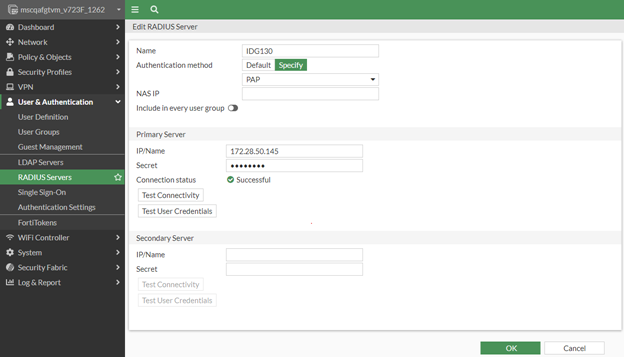
In the Create RADIUS Server page, do the following:
In the Name field, enter the name of the RADIUS server, for example, IDaaS.
In the Primary Server IP/Name field, enter 10.4.21.94.
In the Primary Server Secret field, enter the shared secret.
Note: The shared secret must be the same value entered the IDaaS Fortinet-FortiGate application page.
For the Authentication Method, click Specify.
Select the required authentication method from the Method drop-down menu, for example PAP.
Click OK.
Step 2b: Create a RADIUS userStep 2b: Create a RADIUS user
You need to create user accounts on the FortiGate unit to define the authentication with an external authentication server (RADIUS). There are several different types of user accounts with slightly different methods of authentication.
Create a RADIUS user account
In the FortiGate Web console, navigate to User & Device > User Definition and then click Create New. The Users/Groups Creation Wizard appears.
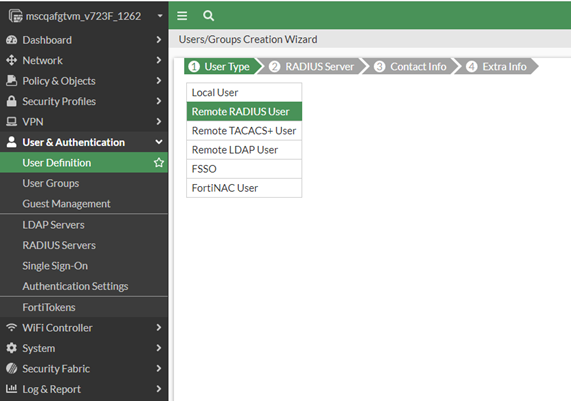
Select Remote RADIUS User and then click Next. The RADIUS Server page appears.
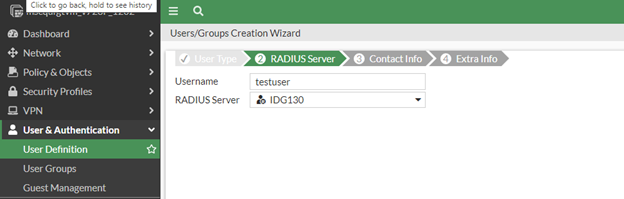
In the User Name field enter the name of the user.
From the RADIUS Server drop-down list, select the RADIUS server you created in the section, Creating a new RADIUS server.
Click Next to move to the Contact Info section and then click Next again to go to the Extra Info section.
In the Extra info section, turn on Enable User Account and then click Submit.
The RADIUS user is created and is listed in the User Definition page.
Step 2c: Create a RADIUS user groupStep 2c: Create a RADIUS user group
Create a RADIUS user group
In the FortiGate Web console, navigate to User & Device > User Groups and then click Create New. The Edit User Group page appears.
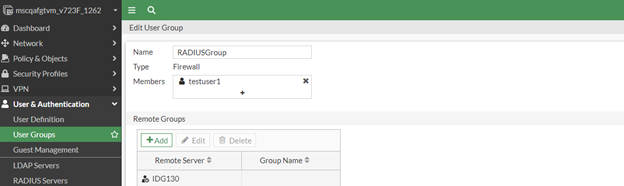
In the Edit User Group page, do the following:
In the Name field enter the group name, for example, RADIUS_users.
In the Type option, select Firewall.
In the Members section select the user you created in the section, Create a RADIUS user.
Click OK.
The RADIUS user group is created and is listed in the User Groups page.
Step 3: Configure the remote authentication timeout
The default timeout is 5 seconds; however, this timeout is insufficient when using Entrust Mobile Soft Token and Mobile Smart Credentials Push. Run following commands from the command line to increase the timeout. The timeout should be greater than Entrust Push timeout settings.
config system global
set remoteauthtimeout 100
end
Step 4: Configure the SSL VPN and policy
In any firewall user group, you can enable SSL VPN access and select the web-portal that the users can access. When the user connects to the FortiGate unit through HTTPS on the SSL VPN port (default 10443), the FortiGate unit requests a username and password.
SSL VPN access also requires an SSL VPN security policy (action is SSL VPN) with an identity-based rule enabling access for the user group.
Step 4a: Configure the SSL VPNStep 4a: Configure the SSL VPN
Configure the SSL VPN
In the FortiGate Web console, navigate to VPN > SSL-VPN Portals, select full-access and then click Edit. The Edit SSL-VPN Portal page appears.

Disable the Split Tunneling, as shown above.
Click OK.
Navigate to the SSL-VPN Settings.
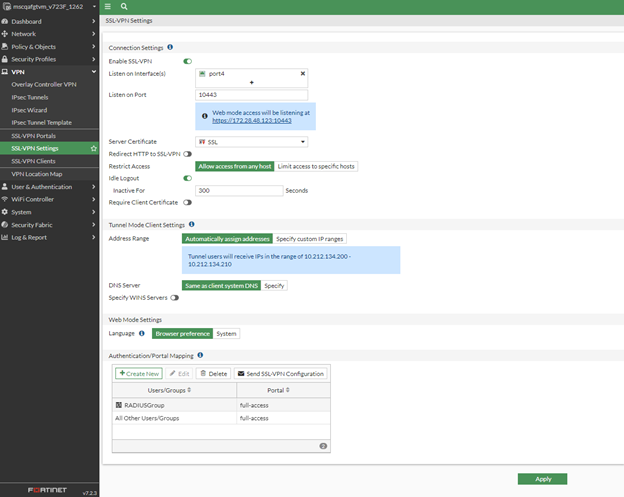
Under Connection Settings, do the following:
From the Listen on Interface(s) field, select the external Interface-Internet Connected (WAN).
In the Listen on Port field enter 10443.
For Restrict Access, select Allow access from any host.
From the Server Certificate drop-down menu, select the Fortinate built-in certificate, Fortinet-Factory. Ignore the warning.
Under Authentication/Portal Mapping, click Create New. The New Authentication/Portal Mapping page appears.
In the New Authentication/Portal Mapping section do the following:
Under Users/Groups select the RADIUS users group that you created in the section, Create a RADIUS user group.
From the Portal drop-down menu, select full-access from the drop-down list.
Click OK.
In the Authentication/Portal Mapping section, select web-access for All Other Users/Groups and then click Apply.
Step 4b: Create an SSL VPN policyStep 4b: Create an SSL VPN policy
Create an SSL VPN policy
In the FortiGate Web console, navigate to Policy & Objects > Firewall Policy and then click Create New. The New Policy page appears.
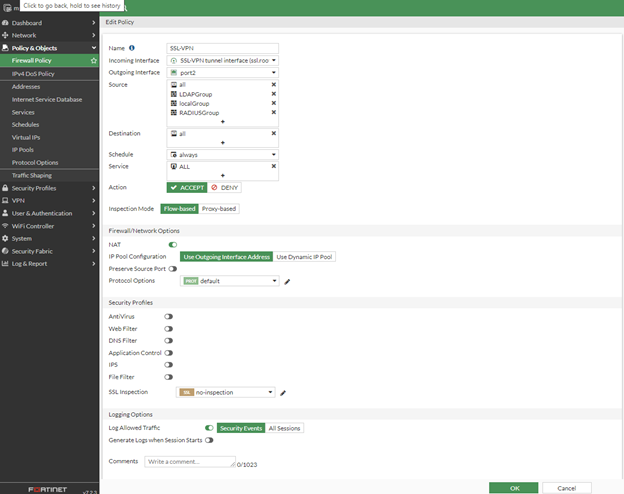
In the New Policy page, do the following:
In the Name field enter the name of the policy, for example, SSL-VPN.
For the Incoming Interface, select SSL-VPN tunnel interface.
For the Outgoing Interface, select Internal Network Interface (LAN).
For Source select all and the RADIUSuser group that you created in the section, Create a RADIUS user group.
For the Destination Address, select All.
For the Schedule, select Always.
For the Service, select Always.
For the Action, select Accept.
Leave the remaining settings at the default values.
Click OK.
Step 5: Configure an IPsec VPN and policy
An IPsec VPN can be configured to accept connections from multiple dynamically addressed peers. You would do this to enable employees to connect to the corporate network remotely. On a FortiGate unit, you create this configuration by setting the Remote Gateway to Dialup User. A VPN tunnel has one end on a local trusted network, and the other end is at a remote location. The remote peer (device) must be authenticated to be able to trust the VPN tunnel. The pre-shared key is used to authenticate each other with IPsec VPN.
Step 5a: Configure the IPsec VPNStep 5a: Configure the IPsec VPN
Configure the IPsec VPN
In the FortiGate Web console, navigate to VPN > IPsec Wizard. The VPN Wizard launches.
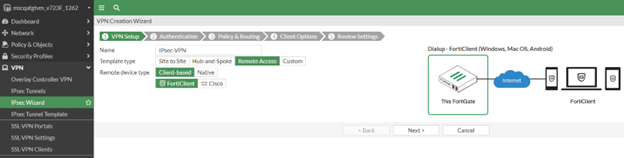
In the Name field, enter the VPN name, for example IPsec VPN Name.
For the Template Type, select Remote Access.
For the Remote Device Type, select the FortiClient.
Click Next. The Authentication page appears.
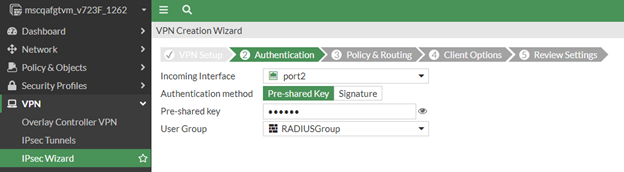
In the Authentication page, do the following:
For the Incoming Interface, select the FortiGate External Interface-Internet Connected (WAN).
For the Authentication Method, select Pre-shared key.
Enter the Pre-shared key password.
From the User Group drop-down menu, select the RADIUS user group you created in Create a RADIUS user group.
Click Next. The Policy and Routing page appears.
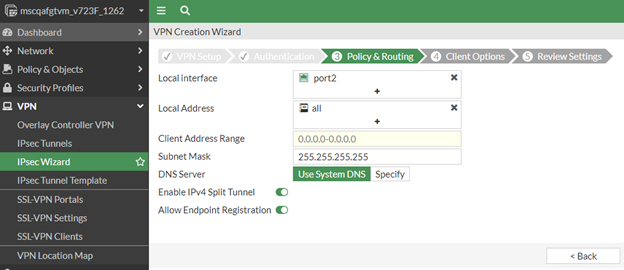
In the Policy and Routing page, do the following:
For the Local Interface, select the FortiGate Internal Interface (LAN).
For the Local Address, select All.
In the Client Address Range field, enter the IP address range for VPN client adapter,
for example, 10.0.0.2-10.0.0.250.
In the Subnet Mask field, enter the IP Range, for example, 255.255.255.0.
Leave the remaining settings at the default values.
Click Next. The Client Options page appears.
In the Client Options page, click Next.
Click Next. The Review Settings page appears.
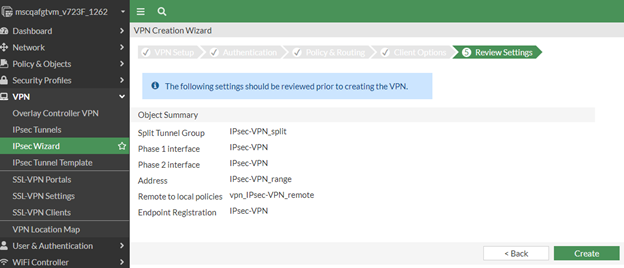
In the Review Settings page, click Create.
An IPsec VPN policy is created automatically during the configuration process. The next step in the configuration process is to modify the IPsec VPN policy.
Step 5b: Modify the IPsec VPN PolicyStep 5b: Modify the IPsec VPN Policy
Modify the IPsec VPN policy
In the FortiGate Web console, navigate to Policy & Objects, Firewall Policy.
Select the IPsec VPN Policy and click Edit. The Edit Policy page appears.
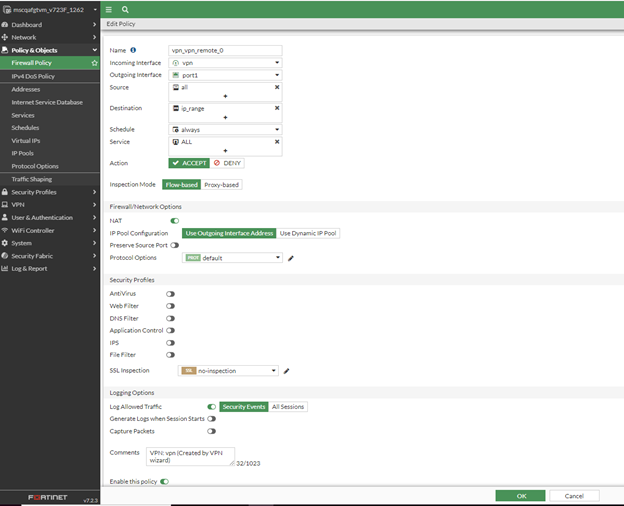
In Edit Policy page, change the Source field to ALL and then click OK.
Step 6: Add FortiClient VPN connections
Download the FortiClient software from the Fortinet web and install on it on a Client Computer. After installing the FortiClient, you need to add a VPN connection.
Step 6a: Add the FortiClient SSL VPN connectionStep 6a: Add the FortiClient SSL VPN connection
Add the FortiClient SSL VPN connection
Launch the FortiClient software and click Configure VPN. The New VPN Connection page appears.
In New VPN Connection page, select the SSL-VPN tab and do the following:
In the Connection Name field, enter the name for the connection, for example, SSL_VPN.
In the Remote Gateway field, enter the IP address for the FortiGate External interface IP (WAN).
Click the Customize port checkbox and enter the port number 10443.
Select the Prompt on Login option for Authentication.
Leave the remaining settings at the default values.
Click Apply and then click Close.
Step 6b: Add an IPsec VPN connectionStep 6b: Add an IPsec VPN connection
Add the FortiClient IPsec VPN connection
Launch the FortiClient software and select Add a new connection from Settings drop-down list. The New VPN Connection page appears.
In the New VPN Connection page, select the IPsec VPN tab and do the following:
In the Connection Name field, enter the name for the connection, for example, IPsec_VPN.
In the Remote Gateway field, enter the IP address for the FortiGate External interface IP (WAN).
From the Authentication Method drop-down menu, select Pre-shared key and enter the same key you created in the section, Configure the IPsec VPN.
Select the Prompt on Login option for Authentication (XAuth).
Leave the remaining settings at the default values.
Click Apply and then click Close.
Step 7: Add Fortinet-FortiGate to IDaaS
Add Fortinet-FortiGate to Identity as a ServiceAdd Fortinet-FortiGate to Identity as a Service
Note: Entrust recommends that when multiple RADIUS applications are configured that each RADIUS application is given a unique shared secret.
Integrate a RADIUS client
Click ![]() > Security > Applications. The Applications page appears.
> Security > Applications. The Applications page appears.
Click Add. The Select an Application Template page appears.
Do one of the following:
Select RADIUS and VPN Integrations from the search drop-down list and scroll to find the application you want to add to IDaaS.
- or -
In the Search bar, enter a search option to filter for the application you want to add to IDaaS.
Click Fortinet. The Add Fortinet page appears.
Optional: Edit the Application Name.
Optional. Enter a Description for your application.
Optional. Add a custom application logo as follows:
Click ![]() next to Application Logo. The Upload Logo dialog box appears.
next to Application Logo. The Upload Logo dialog box appears.
Click ![]() to select an image file to upload.
to select an image file to upload.
Browse to select your file and click Open. The Upload Logo dialog box displays your selected image.
If required, resize your image.
Click OK.
Click Next. The Setup page appears.
Click Add to next to Hosts to add the host name of the VPN server. The RADIUS agent receives the request on this host. The RADIUS Agent on the Gateway determines the RADIUS application the request is for based on the host name and port.
Enter the host name in the Host dialog box and then click OK. Repeat this step to add more host names.
In the Port field, enter the port on which the RADIUS agent accepts messages.
Tip: Do not enter 8443 as the port number for this application. Port 8443 is used by the Entrust Identity Enterprise agent in your Gateway.
Attention: The RADIUS agent uses the host name that sent a request and the port number that it received the request from to determine which RADIUS application made the request. Because of that:
–Two RADIUS applications with the same port value cannot share any host names.
–Two RADIUS applications that have one or more matching host names must have different port values.
In the Shared Secret field, enter the shared secret that is used by your VPN server. This is the RADIUS secret shared between your VPN server and the RADIUS server. The shared secret value must match a shared secret in your RADIUS client.
From the Select RADIUS Agent drop-down list, select the name of the Gateway containing the RADIUS agent to which this application will be assigned.
Optional: From the Select RADIUS Attribute for IP Address drop-down list, select the RADIUS attribute that corresponds to your IP location.
In the Challenge Response Queue Max Time field, set the number of seconds that the RADIUS agent waits for a response to first-factor authentication. The default value is 180 seconds.
In the Challenge Response Queue Max Size field, set the maximum number of second-factor challenge requests allowed in the queue of your RADIUS application. The default value is 1000 requests. The maximum value is 10,000.
In the Request Cache Timeout field, set the number of seconds to cache requests. The default value is 10 seconds.
From the Character Set drop-down list, select the character set used to decode and encode string values (including the user ID and password values) in RADIUS messages. The options are UTF-8 and ISO-8859-1.
Optional: Select Log RADIUS messages to enable RADIUS message logging. When enabled, messages for the RADIUS agent are logged to the same log file as the gateway logs.
Optional: Enable the Authentication Settings.Optional: Enable the Authentication Settings.
Select Enable Push Authentication Fallback if you want to authentication to fallback to another authenticator in the event of a failure. If required, set the Push Authentication Fallback Timeout to the number of minutes before the push authentication times out.
Select When authenticating the user will be asked to select their second-factor authenticator. When selected, after the user responds to the first-factor challenge, they are prompted to select their second-factor authenticator. The list of available second-factor authenticators is set by the resource rule.
The following is a list of supported strings matched to the authentication types:
Grid: grid
Knowledge-based Authentication: kba
One-time password: email, sms, voice
Smart Credential Push: scpush
Temporary Access Code: tac
Token: token
Token push: push
Select Indicate if requests must include the message-authenticator attribute for incoming messages to include the message-authenticator attribute for incoming messages.
Select Indicate if requests must include the message-authenticator attribute for outgoing messages to include the message-authenticator attribute for outgoing messages.
Select Remove domain from user ID for incoming requests to remove the domain value from the user ID during authentication when the user ID provided by the RADIUS client is in the format domain\username and the user ID in IDaaS is in the format username.
Select Indicate if Active Directory password authentication requests are handled by the same Gateway Instance that initiated the request to require that Active Directory password authentication and change requests that are initiated as part of the RADIUS authentication are handled by any Gateway Instance in the same Gateway cluster that initiated it. If disabled, the request is handled by any Gateway Instance.
Select Enable one-step multi-factor authentication. When enabled, the user enters their user ID and then their password and token response in the password field. If you select this option, second factor authenticators available in the resource rule are limited to token and temporary access code.
Enter the One-step multi-factor authentication security token length. This is the length of the token or temporary access code response if you enable one-step multi-factor authentication.
Optional. Add Response Attributes.Optional. Add Response Attributes. Response attributes are returned to the RADIUS application after successful authentication. Use this setting to configure RADIUS attributes to return information such as the user's group information to the VPN server.
When adding response attributes, you optionally add group filters. For example:
Example:
Users in IDaaS may belong to one of the following groups CANADA, US, UK, FRANCE.
The VPN server wants the FilterID attribute returned from the IDaaS RADIUS agent to be the value NA or EUROPE, depending on whether the user is in NA (Canada, US) or Europe (UK, France).
To do this, use a RADIUS attribute filter for the FilterID attribute with a Groups value with the following filters:
- match CANADA, replace NA
- match US, replace NA
- match UK, replace EUROPE
- match FRANCE, replace EUROPE
Set the Response Attributes as follows:
Click ![]() Add. The Add a Response Attribute dialog box appears.
Add. The Add a Response Attribute dialog box appears.
Select the RADIUS Attribute ID from the drop-down list. The option you select depends on your VPN vendor.
Select the Value Type from the drop-down list.
To return a static value specific in the RADIUS attribute definition, select Static and enter a Value in the field and then click Add.
To return the user’s group membership, select Group and then optionally do the following:
- Click Add to add filters.
- Enter the Match and the Replace attribute filters.
- Click Add to add more attribute filters.
- If you add multiple filters, you can drag and drop them in order of preference.
- Select Stop after matching filter if you only want one the filter to return one value. Using the example above, if you want NA to have preference over Europe, make sure to list Canada and US in the list of filters.
- For Multiple Values Per Attribute, enter the Value Separator and then click Add.
Note: If a user belongs to more than one group, you can either add a separate attribute to your RADIUS response for each group or you can combine all of the groups into a single attribute. For example, if the user belongs to G1,G2,G3 then you would
- return a RADIUS response with three attributes
OR
- return a RADIUS response with one attribute and a value like “G1,G2,G3” where the , is defined in the Value Separator setting or a value like “G1 G2 G3” where the Value Separator is defined as a space.
Attention: The default group separator is a space. If you have group names that are separated by a space, use another separator, such as a comma.
Repeat these steps to add more response attributes.
Optional: Configure the EAP Settings to set up the application to use the EAP RADIUS authentication protocol.
Select EAP Enabled to allow the RADIUS application to accept EAP messages.
When enabled, authentication messages with EAP content are treated as EAP requests. The application can accept only EAP authentication requests.
When disabled, incoming authentication requests are processed by the RADIUS application as a standard RADIUS authentication request (even if the request includes EAP content). In this case, the application can accept only standard RADIUS authentication requests.
Select the EAP Protocol from the drop-down list. The options are PEAPv0 with MS-CHAPv2 and PEAPv1 with GTC.
This setting defines the type of EAP authentication protocol that is performed on EAP requests received by the RADIUS application. Consult the configuration requirements of your VPN server to determine which EAP protocol to select.
Select Return MPPE Keys to include the MPPE (Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption) recv and mppe send keys in the Access-Accept message returned during a successful EAP authentication. The setting is enabled by default.
Select Use PEAPv1 label when calculating MPPE Keys to use the PEAPv1 label when calculating the mmpe recv and mppe send keys.
Leave the Minimum TLS Version, Maximum TLS Version and Allow Weak Ciphers at the default settings unless you have an older VPN and need to configure these settings to allow older versions of TLS or weaker ciphers to interoperate with older VPN servers that do not support the latest versions.
Configure the Deprecated Settings if your RADIUS application is connected to a Gateway version older than 3.0. These values are only required for backwards compatibility.
Select Token OTP Only, Password with second-factor, or No first-factor as the Authentication Type. This setting defines the level of authentication required to access a RADIUS application that relies on a gateway RADIUS agent configured before release 3.1.
Note: MSCHAPv2 authentication is not supported when No first-factor authentication is configured for the RADIUS application.
Click Submit.
Step 8: Protect Fortinet-FortiGate with a resource rule
Add a resource rule
Step 9: Test the integration
Test the authentication using FortiClient SSL VPNTest the authentication using FortiClient SSL VPN
Launch the FortiClient software and select SSL-VPN from the Connection drop-down menu.
Enter the RADIUS Username and Password, then click Connect.
Enter a response to the grid challenge, then click OK.

The user authenticated successfully and a SSL VPN Connection is established.
Test the authentication using FortiClient IPsec VPNTest the authentication using FortiClient IPsec VPN
Launch the FortiClient software and select IPsec-VPN from the Connection drop-down menu.
Enter the RADIUS Username and Password, then click Connect.
Enter a response to the token challenge, then click OK.
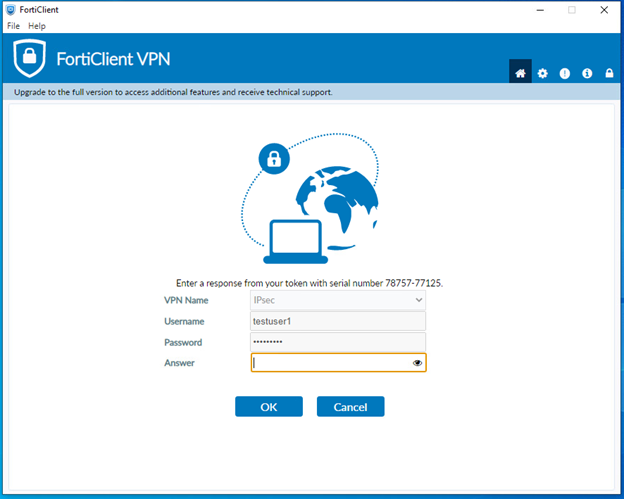
The user authenticated successfully and the IPsec VPN connection is established.
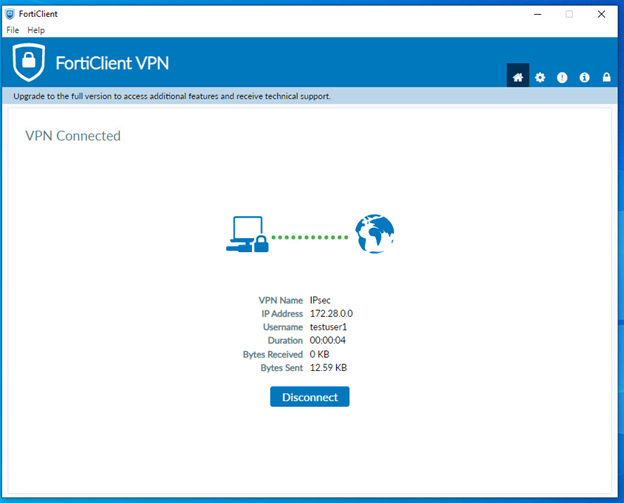
Test using mobile soft token authenticationTest using mobile soft token authentication
Log in with the correct first-factor username/password on the FortiClient SSL or IPsec-VPN Connection.
Open the Entrust Identity app on your mobile device.

Click the Actions button at the bottom of the screen if you have not received a new transaction notification.

Click Confirm.